It is no secret that good nutrition is very important during pregnancy and breastfeeding period.
Obviously, the best way to nourish the body is eating real nutrient dense foods. You can get all your vitamins and minerals from whole real foods.
However, sometimes out diet may not be perfect and we start to look for alternatives in the form of prenatal vitamins.
How to choose the right one?

What to pay attention in Prenatal Multivitamin Supplements?
Check the ingredient list! Make sure it contains vitamins and minerals in natural forms (not synthetic ones) and in right amounts.
While analyzing each vitamin type, I also included best food sources for each of them. Real food is always better than supplements!
1. Folate or Folic acid?
Make sure your supplement contains Folate, not Folic acid.
ONLY purchase these forms of methylfolate which are biologically active (bioavailable):
- Metafolin
- L forms
- L-5 forms
- L-Methylfolate calcium
- 6(S) forms
- Levomefolic Acid
- Quatrafolic- The 4th generation L-methylfolate glucosamine
The below forms of methylfolate are not metabolized by the body and reduce the bioavailability of L-methylfolate.
AVOID purchasing these forms of methylfolate which are NOT bioavailable:
- 6(R) forms
- D forms
Folate (Vitamin B9) is a very important nutrient, especially during pregnancy.
Folate deficiency may cause serious birth defects of the spinal cord and the brain, and may pose a risk of stroke and cardiovascular disease.
Folic acid is a synthetic form of folate, which has to be changed in the body through several steps before it becomes a folate. Unfortunately, some people cannot metobolize folic acid properly, which leads to a buildup of unmetabolized folic acid. Latest research studies show that too much synthetic folic acid may increase the chances of getting cancer. (source)
Women planning to get pregnant should be consuming 800-1200 mcg of folate per day during several months before they decide to conceive.
Daily recommendation of folate for pregnant women is 600-800 mcg per day.
Folate is naturally found in whole food sources and is also called “tetrahydrofolate”.
Good food sources of folate: 1 cup of cooked black eyed peas contain about 356 mcg of folate, 1 cup of cooked lentils contain about 358 mcg of folate, 1 cup of cooked spinach contains about 263 mcg, 1/2 cup of cooked asparagus contains 134 mcg, 100 gr of avocado contains 122 mcg of folate, 1/2 cup of cooked brocolli has about 84 mcg of folate, 1 orange contains 47 mcg, 1 cup of shredded lettuce contains about 64 mcg of folate, 1 cup of cooked beets contain about 148 mcg,
Best food sources of folate: calf’s liver, chicken liver, duck liver. 1/2 cup of liver provides about 600 mcg of folate! Choose grass-fed and pastured liver.
Best Folate supplements: Pure Encapsulations – Folate 400, Thorne Research – 5-MTHF 1 mg Folate, Doctor’s Best Fully Active Folate with Quatrefolic
The below supplements contain the right forms of folate, however they contain Magnesium stearate or other controversial ingredients.
Other (good) Folate supplements: EZ Melts Folate, 1,000 mcg, Dissolving Tablets, Solgar – Folate (as Metafolin) 800mcg Tablets, One Elevated Methyl Folate+
Read more about folate vs folic acid here: “Folate or Folic acid?”
2. Vitamin B12: Methylcobalamin or Cyanocobalamin?
Vitamin B12 is an important nutrient for nerve health and the construction of red blood cells.
There are two forms of vitamin B12 in supplements – methylcobalamin and cyanocobalamin.
Cyanocobalamin is a synthetic substance made in laboratories and it costs 100 times cheaper than methylcobalamin. It contains cyanide molecule which must be removed by your liver, because cyanide is toxic. Cyanocobalamin does not occur in nature naturally, but it is used in many supplements because of the lower cost. Cyanobalamin is a low quality and slightly toxic form of vitamin B12, which has to be turned into methylcobalamin by the liver.
Methylcobalamin is the proper form of vitamin B12 you should be taking. Methylcobalamin absorbs better, contains no cyanide, and supports production of SAMe (S-adenosyl methionine).
Check your supplement and make sure it contains vitamin B12 in the form of Methylcobalamin, not Cyanocobalamin.
Food sources of Vitamin B12: clams (1401% daily value (DV) in 3 oz), liver (1214% DV in 3 oz), oysters (408% DV in 3 oz), mussels (340% DV in 3 oz), mackerel (269% DV in 3 oz), salmon (257% DV in 3 oz), sardines (126% DV in 3 oz), beef (113% DV in 3 oz), lamb (45% DV in 3 oz), eggs (9% DV in 1 large (50g) egg).
3. Vitamin D and vitamin K2
Make sure vitamin D is in the form of vitamin D3 (Cholecalciferol or calciol), not vitamin D2 (Ergocalciferol) in your prenatal multivitamin supplement. Also, make sure the supplement contains vitamin K2, because vitamin D and vitamin K2 work together. Lack of vitamin K2 may cause vitamin D toxicity. (source)
Supplemental vitamin D comes in two forms: vitamin D2 (Ergocalciferol) and vitamin D3 (Cholecalciferol). Both of these forms need to be converted into a more active form in the body, and vitamin D3 is converted 500% faster than vitamin D2.
Vitamin D3 influences about 3000 genes in the body, so it is especially important to get adequate amounts of it during pregnancy.
Best source of vitamin D comes from a safe sun exposure. It is impossible to overdose vitamin D when you get it from the sun.
When you take oral vitamin D, you need to consume vitamin K2 through food or a supplement too. Vitamin D and vitamin K2 work synergistically.
Vitamin K2 is also very important during pregnancy. Vitamin K2 helps with the development of primary and adult teeth, healthy facial form and the skeleton. Vitamin K2 has no toxicity issues, so it can be doubled or tripled (source).
Many foods naturally high in calcium also contain naturally high amounts of vitamin K2!
Best food sources of vitamin D: cod liver oil, egg yolk, raw milk, fish (salmon, sardines).
Best food sources of vitamin K2: grass-fed dairy, grass-fed butter, pastured eggs, fermented foods, liver.
4. Iron
Iron deficiency anemia is very common during pregnancy, but it is important to get screened before you decide taking iron supplements.
If you consume more iron than your body needs, it may lead to serious iron toxicity. However, having too little iron can have serious health consequences too.
Low iron levels can be addressed by eating naturally iron-rich foods (ex., clams, liver, red meat), and vitamin C can help improve the bioavailability of iron in the food. Calcium binds with iron, so avoid combining calcium-rich foods with iron-rich foods.
Avoid supplements designed to protect against oxidative stress (milk thistle, green tea, etc) while you try to fix the anemia issue, because those kind of supplements cause iron to get directed into ferritin instead of hemoglobin, which may hurt your ability to resolve anemia (source).
All forms of iron supplements can be dangerous if overdosed. A better forms of iron are carbonyl iron, liposomal iron, heme iron. You may want to avoid Ferrous sulfate, as it is relatively toxic and may lead to acute overdose easily (source).
5. Magnesium
Magnesium is one of the most important nutrients and most people do not realize they are deficient in it.
Morley M.Robbins, the founder of “The Magnesium Advocacy Group”, states that Magnesium is the most important nutrient along with air and water.
Morley Robbins does not recommend taking Magnesium Citrate, as it may interfere with Ceruloplasmin and can cause iron dysregulation.
He suggests Magnesium Glycinate by Pure Encapsulations and Jigsaw Magnesium w/SRT as most bio-available Magnesium supplements.
Avoid: Magnesium Citrate (and any other citrates). Small amounts might be okay, but not okay for regular consumption.
Other forms of Magnesium like magnesium glycinate, magnesium malate, magnesium oxide (in small doses), magnesium taurate, magnesium ororate, magnesium threonate are okay (more info).
6. B vitamins
B vitamins are important during pregnancy, however you can easily get them from food.
You can get B vitamins from natural sources like Bee pollen (1/2 tsp a day), beef liver (4-6 oz weekly) (source).
Pure Bee Pollen contains at least 18 vitamins, 25 minerals, 59 trace elements, 22 amino acids, 11 enzymes or co-enzymes, 14 fatty acids, 11 carbohydrates and about 25% protein. Bee pollen is very rich in carotenes and B complex vitamins.
7. Vitamin C
Pure Ascorbic acid is very acidic, so it is best to consume buffered vitamin C like sodium ascorbate which has higher pH.
Some vitamin C powders may come from GMO sources, so pay attention to the source as well.
8. Vitamin A
Choose Vitamin A in the form of Beta Carotene (the natural form) instead of the synthetic form called Retinyl Palmitate. However, it is still might not be the best choice.
There are about 600 known forms of naturally occurring carotenoids, all of them which can be labeled as Vitamin A. Beta carotene and lutein are most well known among those carotenoids.
While beta carotene in supplements is considered as a natural form of vitamin A, it is still not guaranteed that your body can convert it to vitamin A efficiently.
How about synthetic vitamin A? Studies show that even small amounts of synthetic vitamin A Palmitate (Retinyl Paltimate, Retinol Palmitate) might be toxic. Overdose of synthetic vitamin A may cause serious imbalances over time, including birth defects (source).
It is best to get Vitamin A from food, as not everybody can convert beta carotene in supplements to vitamin A efficiently.
To digest carotenes you need healthy fats, so make sure to include some grass-fed butter or grass-fed cream with your fruits and vegetables.
You can also get natural Vitamin A from good quality cod liver oils like Rosita, Nordic Naturals Arctic, Green Pastures Blue Ice.
Best food sources of natural Vitamin A: cod liver oil, liver, grass-fed butter, egg yolks.
9. Pay attention to other ingredients like fillers, binders, lubricants used in the supplement
Avoid fillers like partially hydrogenated and hydrogenated oils, artificial colors, magnesium stearate, and titanium dioxide.
You can find the “other, or inactive ingredients” at the bottom of the supplement panel. These other ingredients are used to fill, bind, and lubricate tablets or capsules.
Sometimes, the value of the overall formula may outweigh the use of a few less harmful binders or fillers, but there are some ingredients that you need to definitely avoid.
The ingredients that are never acceptable are artificial colors, hydrogenated oils, partially hydrogenated oils, and titanium dioxide.
There are controversial opinions about Magnesium stearate. Some studies show that Magnesium stearate will create a biofilm in the body. This biofilm blocks the absorption of needed nutrients in the body.
Popular Prenatal Multivitamin Supplements (Pros and Cons)
All of the below supplements are low in magnesium. Most people are deficient in Magnesium, so you may want to consider it.
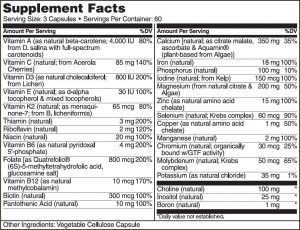
NATURELO Prenatal Whole Food Multivitamin (Vegan)
Naturello Prenatal Whole Food Multivitamin is a natural plant-based supplement, which is also GMO-free.
I think this is one of the best prenatal supplements available right now.
Pros:
- Contains bioavalable form of Folate – (6S)-5-methyltetrahydrofolic acid, glucosamine salt)
- Contains natural vitamin C from Acerola cherries
- Does not contain synthetic vitamin A
- Contains vitamin K2
- Contains vitamin B12 in the form of Methylcobalamin
- Contains 1 mg of Boron
- Does not contain fillers or stearates
- Sugar free
Cons: did not find any
Special notes:
- Serving size is 3 capsules
- Vegan
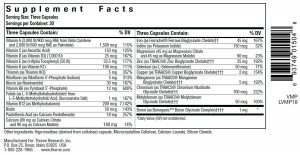
Thorne Basic Prenatal (Vegetarian capsules)
Thorne prenatal contains the right form of Folate and other high quality ingredients. Overall, a great prenatal multivitamin supplement!
Pros:
- Contains bioavailable form of Folate (L-5-Methyltetrahydrofolate) instead of synthetic Folic acid.
- Contains Methylcobalamin, instead of Cyanocobalamin for vitamin B12.
- Contains chelated Iron (Ferrous Bisglycinate Chelate) and Iodine.
- Contains other chelated minerals.
- Contains 1 mg of Boron.
- It has high amounts of each vitamin and mineral.
- The ingredients are natural and GMO-free.
- No Stearates, no synthetic colors, no artificial preservatives.
- Gluten free, egg free, nut free.
Cons:
- Contains Palmitate (synthetic form) along with Beta carotene (natural form) as vitamin A
- Contains Ascorbic acid. Buffered vitamin C would be better.
- Does not contain vitamin K2, but contains K1.
Special notes:
- Serving size is 3 capsules a day
- Vegetarian capsules
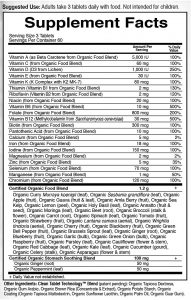
Garden of Life Organic Prenatal Multivitamin Supplement (Kosher, Vegan Tablets)
Garden of Life My kind prenatal multivitamin supplement is a very popular one. It has a great ingredient list, however there are some concerns about the form of folate in it. When isolated from food, folate converts to folic acid. While it’s not synthetic, if you have any methylation mutations, you body won’t be able to reduce it back into usable folate.
Pros:
- The ingredients are plant-based and mostly from organic fruit and vegetable blends!
- Contains Methylcobalamin as Vitamin B12
- Does not contain synthetic vitamin A palmitates
- Contains vitamin K2 (MK-7)
- Contains ginger and peppermint, which may help with morning sickness
- It provides 18 mg of food based iron, and other essential vitamins and minerals.
- No harmful fillers, no stearates
- Certified organic
- Vegan
Cons:
- It has oxidized folate which has the same molecular formula as folic acid, while its not synthetic, its still considered folic acid.
Special notes:
- Serving size is 3 tablets
- Vegan tablets
As a summary, this is still one of the best prenatal multivitamin supplements available on the market. The only concern is the form of folate in it, which may not be the most bioavalable form available.
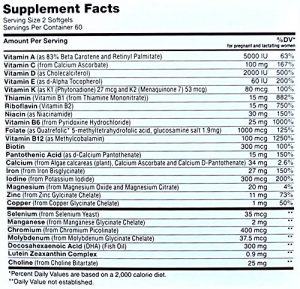
Zahler Prenatal + DHA with Folate (Kosher)
Zahler prenatal + DNA supplement is kosher certified. It provides the right form of folate (1000 mcg per serving), Iron from Iron Bysglycinate (27 mg), Methylcobalamin as Vitamin B12, Calcium Ascorbate as Vitamin C, and other needed vitamins and minerals.
It provides a little Magnesium, so you may want to supplement with extra Magnesium through food or other supplements.
Pros:
- Contains bioavailable form of folate as Quatrefolic
- Contains buffered vitamin C, not ascorbic acid
- Contains Methylcobalamin, not Cyanocobalamin as vitamin B12
- Contains vitamin K2, along with K1
- No stearates
Cons:
- Contains a small amount of synthetic vitamin A palmitate
Special notes:
- Serving size is 2 softgels
- Certified kosher
- Contains DHA
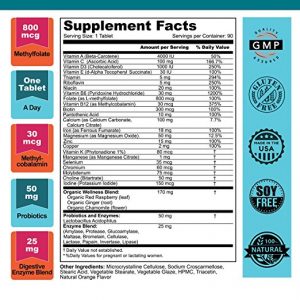
Best Nest Prenatal Vitamin
This supplement provides the right form of Folate, methylcobalamin as Vitamin B12, contains probiotics and enzymes.
This prenatal contains some fillers and binders like stearic acid, and vegetable stearate, which you may not like.
Overall, this is a cost effective prenatal multivitamin supplement with the right form of folate.
Pros:
- Contains folate in the form of L-Methylfolate – bioavalable form.
- Contains Vitamin B12 in the form of Methylcobalamin.
- Contains probiotics and enzymes
- Non-GMO ingredients
Cons:
- Contains some fillers and binders like stearic acid, and vegetable stearate
- Does not contain vitamin K2
- Some minerals are in a “Citrate” form
- Vitamin C is not buffered (ascorbic acid)
Special notes:
- Serving size is 1 tablet
SmartyPants Prenatal Complete Gummy Vitamins
This is another popular mutivitamin supplement with the bioavalable form of folate, however it might not be suitable for everyone. I like the fact that it might be easy to take, however I do not like the synthetic vitamin A, and some other ingredients in this supplement.
Pros:
- In the form of chewable gummies, which probably taste good
- Contains bioavailable form of folate – L-methylfolate (800 mcg)
- Contains Methylcobalamin (vitamin B12), only 10 mcg though
- Contains vitamin K2 (16 mcg)
Cons:
- Contains synthetic vitamin A palmitate (3000 UI)
- Contains unbuffered vitamin C – ascorbic acid
- Contains sugars and citric acid
- Contains Gelatin derived from pork
Special notes:
- Serving size – 6 chewable gummies
- Contains Omega-3, EPA, DHA
- Contains gelatin derived from pork
- Iron free